Creating, Opening, and Saving Images¶
Opening Up Acorn¶
When you first open Acorn you will be greeted by an image similar to this one:
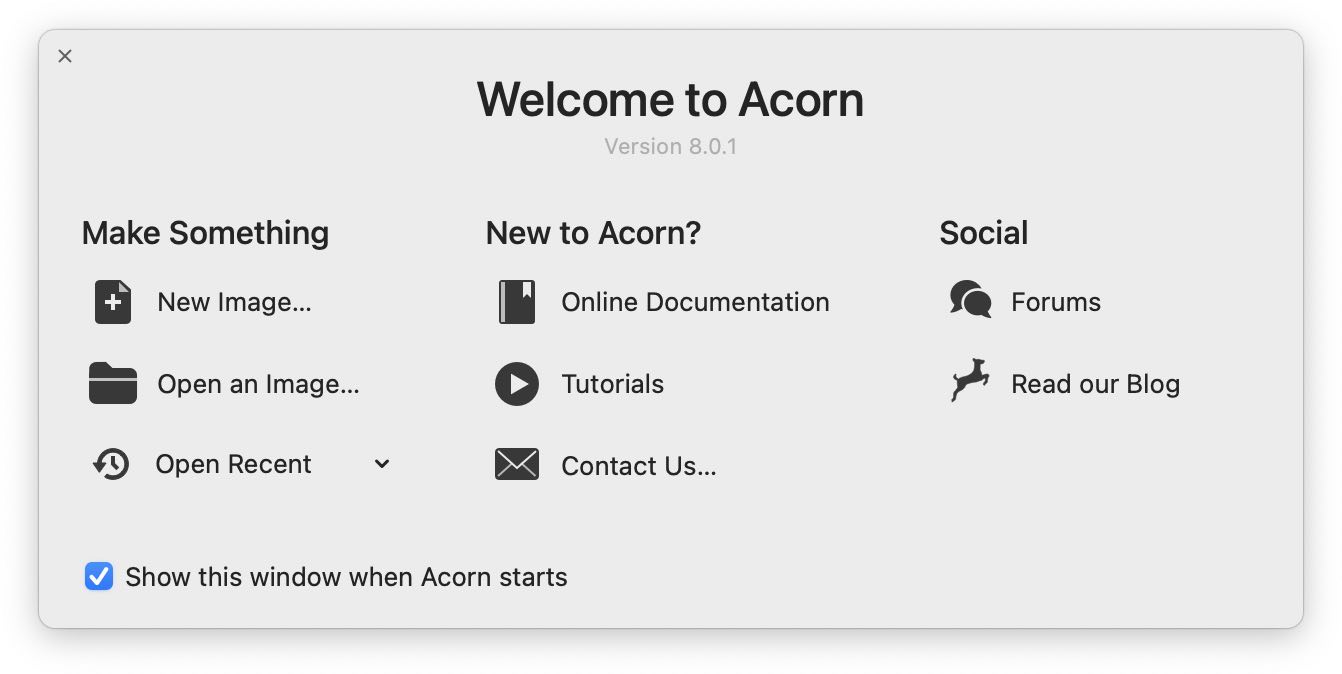
You can choose to create a new image, open an image, or choose from a list of images recently opened in Acorn. If you do not want this window to appear every time you launch Acorn, uncheck the box in the lower left hand corner. If you want this window to re-appear, choose the menu item.
Creating a New Image¶
To create a new image, choose (⌘N) from the menu bar.
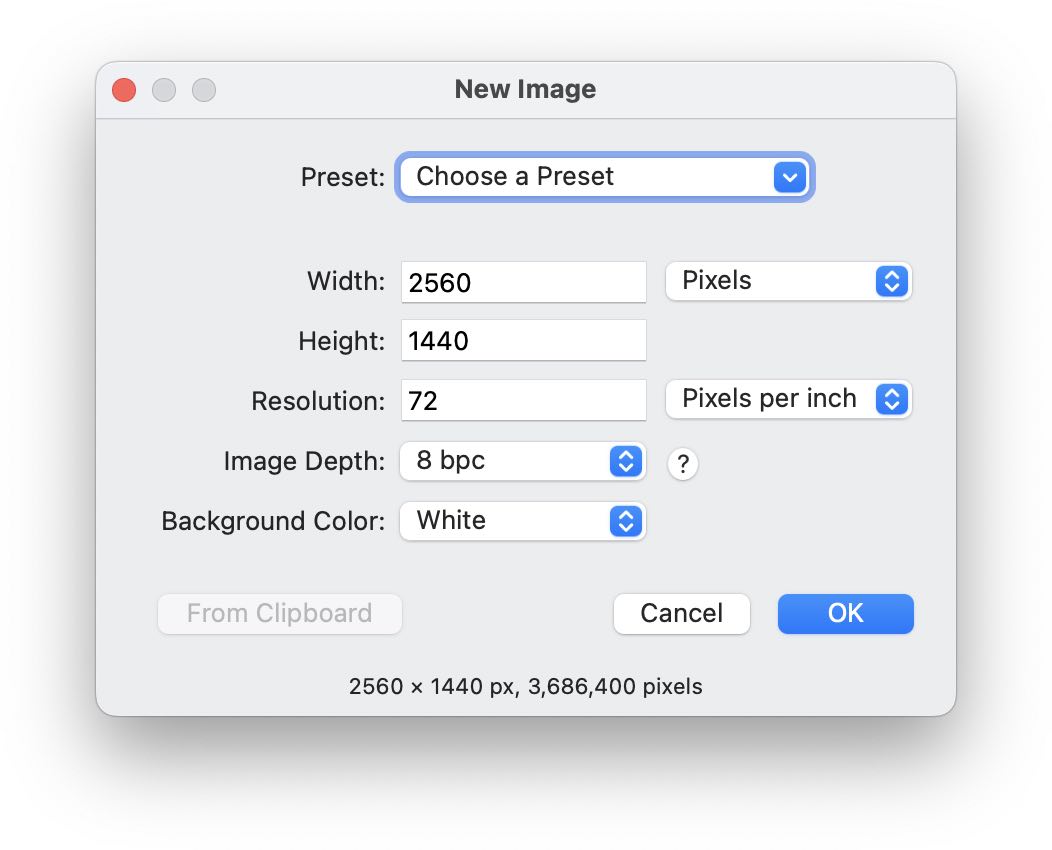
You can choose a preset image size, or you can enter your desired dimensions manually. If you are manually entering the dimensions, you have the option to use different measurement values including pixels, inches, and centimeters. You can also select your image resolution and background color. For more information on resolution and PPI, read all about DPI, PPI, and printing.
Creating and Deleting New Image Presets¶
To create a new image preset, enter the width and height values into the appropriate fields, then click on the preset drop-down menu. Choose 'Save Preset'. You will be prompted to give your preset a name. In order to delete a preset you have created, hold down the Option key while clicking on the preset name. A window will appear to confirm that you want to delete the preset. You can only delete custom presets.
Opening Existing Images¶
To open an image, choose the menu item. You can also drag and drop images onto Acorn's icon in the dock. If you would like to combine two or more images together, use the menu or drag and drop your images from the Finder into Acorn's canvas or layers list. If you add a single image via the menu item and it doesn't fit on the canvas, Acorn will begin a scale and rotate transform for you. The image will automatically be scaled to fit into the canvas. If you want to add the image without scaling, press the ESC key.
If Acorn is running and you have an image on your clipboard that you would like to open in Acorn, right-click on the Acorn icon in the dock and select , or choose from the menu.
If you have a https:// URL to an image on the clipboard, you can choose and the image will download and open in Acorn.
Make sure to read up on Adding Images and Resizing Layers which describes how to combine and resize images.
Tip
If you can only see a small portion of your image, try zooming out using or dragging the slider found on the bottom of the canvas window. Alternatively, you can use . If you are wanting a specific zoom percentage, click on the zoom percentage number located on the bottom of the canvas and enter a value.
Saving Images¶
You can save images by selecting or . When working with an image editor such as Acorn, it is a good idea to always work off a copy of an image rather than the original. When in doubt, select and re-name the file so you don't accidentally make permanent changes to your original image! Also, be aware that saving certain file types will “flatten” layers so that you cannot edit them later. Acorn will warn you if you are at risk of losing layers when saving, unless you have checked the 'do not show this message again' box.
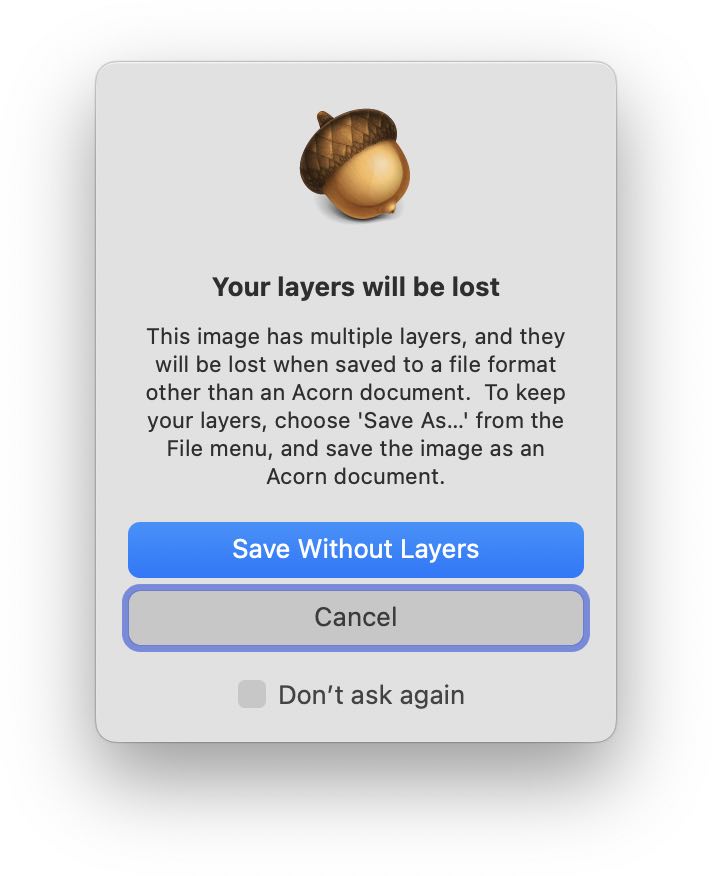
When in doubt, be sure to save a copy of your file as .acorn.
Autosave and Versions¶
Acorn gives you the ability to use autosave and access previous versions of your image using Time Machine. Autosave is on by default, but can be disabled in Acorn's Settings under the General tab. With autosave, your changes are saved automatically for you. Versions of your image will automatically be created every hour and every time you open the file.
To view previous versions of your file, use the menu item.
Image File Formats Acorn Supports¶
Acorn¶
Acorn files are the native file type of Acorn. This is the most robust file format that Acorn supports. When saving in this format all of your layers, grid settings, text and shapes are saved. You are able to edit them when you re-open the image. This is the recommended format for editing images with layers in Acorn. If in doubt, save your image in this format.
The file extension for Acorn images is .acorn.
AI¶
AI stands for Adobe Illustrator Artwork. Acorn can open Adobe Illustrator files that have been saved with PDF compatibility turned on. Acorn cannot save or export images in the AI format.
The file extension for AI is .ai
Read more about Adobe Illustrator files on Wikipedia.
BMP¶
BMP is a popular image format on Microsoft Windows.
The file extension for BMP is .bmp
Acorn can read and write BMP images.
GIF¶
GIF stands for Graphics Interchange Format, and is a lossless 8 bit image format. Since GIF files can only use up to 256 colors in an image, you will only want to use this format for specific web applications.
The file extension for GIF is .gif
Acorn can read and write GIF images. Read more about GIF on Wikipedia.
HEIF¶
HEIF stands for high efficiency image file format. A HEIF file can be a single image or a sequence of images.
The file extension is .heif or .heic
Acorn can read and write HEIF files. Read more about HEIF on Wikipedia.
ICO¶
ICO stands for Microsoft Icon. To save a .ico file it must be square and 16, 32, 48, 128, or 256 pixels in size.
The file extension for Microsoft Icon is .ico
Acorn can read and write .ico files. Read more about Microsoft Icon on Wikipedia.
JPEG¶
JPEG is a very popular image format used primarily for photographs. Since JPEG is a lossy format, it is not ideal for graphics with text.
File extensions for JPEG are .jpeg and .jpg. If you prefer to save with the .jpg extension, manually enter it in the “save as” field as the file extension. Acorn will remember that you prefer .jpg over .jpeg next time you save. (Only available in the direct version, due to restrictions Apple places on applications distributed via the App Store).
Acorn can read and write JPEG images. Read more about JPEG on Wikipedia.
JPEG-XL¶
JPEG-XL is a modern image compression standard designed to replace formats like JPEG, PNG, and WebP by offering superior compression efficiency, better image quality, and advanced features. It reduces file sizes by up to 60% compared to JPEG, supports both lossless and lossy compression, and handles modern requirements like HDR, wide-gamut colors, transparency, and animations. JPEG-XL enables efficient transcoding from JPEG without quality loss, simplifies workflows by combining features of multiple formats, and reduces bandwidth and storage needs, making it ideal for web use and eco-friendly. Its versatility and forward-looking design make it a strong candidate for future imaging standards.
The file extension for JPEG-XL is .jxl
Export images as JPEG-XL via the menu.
JPEG 2000¶
JPEG 2000 was designed to be the successor to JPEG, though it is not in use much these days.
The file extension for JPEG 2000 is .jp2
Acorn can read and write JPEG 2000 images. Read more about JPEG 2000 on Wikipedia.
Export via the menu.
KXT¶
KXT stands for Khronos Texture. According to GitHub, “KTX is a lightweight file format for OpenGL® and Vulkan® textures. KTX files contain all the parameters needed for texture loading. A single file can contain anything from a simple base-level 2D texture through to a cubemap array texture with mipmaps.”
The file extension is .kxt
Acorn can write KXT via menu.
OpenEXR¶
Quoting Wikipedia, “OpenEXR, or EXR for short, is a deep raster format developed by ILM and broadly used in the computer-graphics industry, both visual effects and animation. OpenEXR's multi-resolution and arbitrary channel format makes it appealing for compositing, as it alleviates several painful elements of the process.”
The file extension is .exr
Acorn can write EXR via the menu.
PDF¶
PDF stands for Portable Document Format, and is an open standard developed by Adobe Systems. When opening a PDF in Acorn a window will appear allowing you to set the resolution and background color.
The file extension for PDF is .pdf
You can export as PDF via the menu.
Read more about PDF on Wikipedia.
PICT¶
Quoting Wikipedia, "PICT is a graphics file format introduced on the original Apple Macintosh computer as its standard metafile format."
The file extension for PICT is .pict
Acorn can open .pict files. Read more about PICT on Wikipedia.
PNG¶
PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics, and is a lossless 32 bit image format. If you need to have crisp text or transparency in your image, PNG is the way to go.
The file extension for PNG is .png
Acorn can read and write PNG images. To save an PNG file with a reduced palette (aka, an “Indexed PNG”), use the menu.
PSD¶
PSD is the native file type for Adobe Photoshop. Acorn does its best to open PSD images, and if possible, preserve layers. Photoshop layer styles, and editable text are not supported. Vector and text layers are opened as bitmap layers.
The file extension for PSD is .psd
Export via the menu.
RAW¶
Quoting Wikipedia, “A camera raw image file contains minimally processed data from the image sensor of either a digital camera, image scanner, or motion picture film scanner. Raw files are so named because they are not yet processed and therefore are not ready to be printed or edited with a bitmap graphics editor.”
Acorn can import any RAW image that macOS can natively read. Occasionally, Apple will add support for new RAW formats via system updates.
There are many file extensions for RAW files.
See also: RAW Image Support
SVG¶
SVG stands for scalable vector graphics. Acorn offers basic SVG support. You can export documents and shape layers as simple SVG files. If there are no shape layers in your image, then the SVG export option will be grayed out. Additionally, this is a pure vector export— any bitmap operations like layer filters or masks are ignored for SVG export. Acorn can open basic SVG files.
The file extension for SVG is .svg
Export via the menu.
TGA¶
TGA stands for Truevision Graphics Adaptor. If you are running 10.11+ Acorn can open and export your image in the TGA format.
The file extension for TGA is .tga
Export via the menu.
TIFF¶
TIFF stands for Tagged Image File Format. TIFF is a lossless 32, 64, or 128-bit image format and can preserve transparency.
The file extensions for TIFF are .tiff and .tif
Acorn can read and write TIFF images. Read more about TIFF on Wikipedia.
WebP¶
WebP is a file format incorporating both lossless and lossy compression developed by Google.
The file extension is .webp.
Export via the menu.
Other Formats¶
Depending on what version of macOS you are using, Acorn might be able to open up additional image formats. Apple from time to time adds support for new or different formats, and Acorn will usually be able to open up those images automatically.
See Also:¶
Video Tutorials - Saving an Image, Opening Images, Creating New Images